Deces-en-france.fr: 28M Records leak

➤Summary
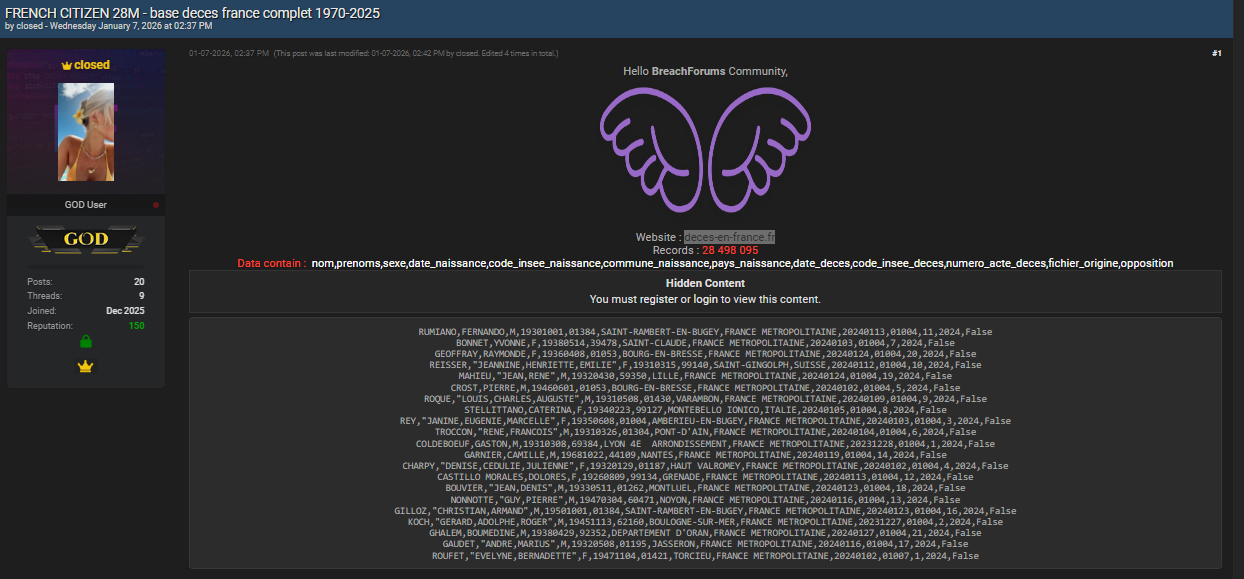
French citizen data breach revelations are raising urgent questions about privacy, data governance, and the growing trade of sensitive records on underground forums. A massive dataset titled “base deces france complet 1970–2025” allegedly involving 28,498,095 records appeared on BreachForums.bf, published on 07.01.2026 by an author using the handle “closed.”
The French citizen data breach centers on deceased individuals registered in France over more than five decades, sourced from public-facing death registries and potentially aggregated beyond their original intent. While the data relates to deceased citizens, the scale, structure, and accessibility of this release present real-world risks, from identity misuse to social engineering. Understanding the context, contents, and implications of this exposure is essential for institutions, researchers, and security teams alike. ⚠️
Overview of the Dataset and Forum Publication
The dataset, promoted under a title referencing France’s national death records, was shared on BreachForums.bf, a well-known underground forum for trading and releasing large data collections. According to the post, the database contains 28,498,095 entries covering deaths between 1970 and 2025. Fields reportedly include name, given names, sex, date of birth, place of birth codes, country of birth, date of death, death location codes, death certificate numbers, source file, and opposition flags. The French citizen data breach claim emphasizes completeness and nationwide coverage, which increases its attractiveness to malicious actors. 🗂️ Such releases are often repackaged and redistributed across multiple channels once published.
What Data Was Allegedly Compromised
Although the records focus on deceased individuals, the compromised data fields are highly structured and standardized. This includes identifiers commonly used in administrative processes, such as INSEE codes and civil registry references. When combined, these elements can enable profiling, correlation with living relatives, or validation of fraudulent claims. The presence of “opposition” indicators suggests attempts to respect opt-out preferences in the original systems, raising questions about how consent and access controls were bypassed or ignored. Analysts tracking underground leaks often include such releases in dark web reports to assess downstream misuse. 📊
Why a Death Records Leak Still Matters
A common question arises: if the data concerns deceased persons, does it really pose a risk? The answer is yes. Even when individuals are no longer alive, their data can be exploited for identity reconstruction, genealogical fraud, or targeted scams against families. Criminals may use death records to craft convincing narratives for inheritance fraud or to bypass verification processes. In the context of a French citizen data breach, the cultural and administrative reliance on civil records amplifies the potential impact. This is why large-scale registry exposures are treated seriously by privacy regulators. 🔍
BreachForums and the Underground Data Economy
BreachForums.bf has become a central marketplace and bulletin board for large datasets, ranging from corporate leaks to government-related records. Posts often include samples to prove authenticity and encourage redistribution. Monitoring such platforms allows defenders to compare dark web monitoring approaches and evaluate which sources provide early warning signals. The publication of this dataset follows a familiar pattern: a short description, record count, and claim of completeness. Over time, such data may migrate to private channels or be bundled with other leaks, complicating containment efforts. 🌐
Legal and Regulatory Context in France
France enforces strict data protection standards under the GDPR and national regulations overseen by the CNIL. Even when dealing with deceased individuals, French law recognizes protections for personal data, particularly where it affects the rights of living persons. Aggregating and redistributing civil registry data outside its original purpose can trigger regulatory scrutiny. The French citizen data breach narrative may therefore prompt renewed discussion around open data policies and safeguards. For authoritative guidance on data protection obligations, the CNIL provides extensive resources and enforcement updates, making it a relevant external reference for understanding compliance expectations. 🏛️
Implications for Institutions and Researchers
Public institutions, archives, and research organizations rely on historical records for legitimate purposes. However, incidents like this blur the line between open data and abuse. When datasets are extracted and shared without context or safeguards, they can undermine trust in public data initiatives. Security teams must strengthen data breach detection capabilities to identify when large-scale scraping or aggregation occurs. Integrating external intelligence with internal monitoring helps flag unusual access patterns before data appears on forums. 🛡️
The Role of Intelligence and Monitoring Tools
Security operations increasingly rely on specialized platforms to track underground activity. Teams often evaluate and compare dark web monitoring services to determine which provide actionable alerts rather than noise. Advanced dark web solutions can detect mentions of specific datasets, keywords, or national registries shortly after publication. These insights may later be documented internally as a case study dark web monitoring reference, helping organizations refine response playbooks. Early visibility can reduce reputational damage and inform communication strategies. 🔐
Practical Checklist for Mitigating Registry Data Exposure
To reduce the likelihood and impact of similar incidents, organizations handling large registries should follow a structured approach:
• Limit bulk access to civil registry databases
• Apply rate-limiting and anomaly detection to public interfaces
• Regularly audit data extraction logs
• Monitor underground forums for early signs of exposure
• Establish clear disclosure and response procedures
This checklist supports resilience and aligns with best practices for protecting sensitive structured data. ✅
Industry Perspective and Expert Insight
Privacy experts note that large historical datasets are increasingly targeted because they are perceived as “low-risk” yet highly valuable. One European data protection specialist remarked, “Aggregated records, even of deceased individuals, can enable sophisticated fraud when combined with other leaks.” This viewpoint underscores the need for ongoing monitoring and contextual risk evaluation. Dark web intelligence solutions enable analysts to track how datasets circulate and transform after their initial disclosure.📘
Learning From the French Citizen Records Exposure
The alleged French citizen data breach serves as a reminder that scale alone can transform seemingly benign data into a strategic asset for threat actors. Tracking how the dataset propagates across forums and private channels is essential for impact assessment. Analysts reviewing similar cases often consult repositories and insights available at Darknetsearch to benchmark exposure patterns and response timelines. Transparency and collaboration between regulators, institutions, and security researchers will be key to addressing future incidents. 🚀
Conclusion and Call to Action
This exposure of nearly 28.5 million French death records illustrates how historical and administrative data can become a modern security liability when misused. By strengthening oversight, improving monitoring, and leveraging intelligence-driven insights, organizations can better protect sensitive registries and public trust. Stay informed through reliable dark web intelligence resources and ensure your defenses evolve alongside emerging threats. Discover much more in our complete guide. Request a demo NOW.
Discover how CISOs, SOC teams, and risk leaders use our platform to detect leaks, monitor the dark web, and prevent account takeover.
🚀Explore use cases →Q: What is dark web monitoring?
A: Dark web monitoring is the process of tracking your organization’s data on hidden networks to detect leaked or stolen information such as passwords, credentials, or sensitive files shared by cybercriminals.
Q: How does dark web monitoring work?
A: Dark web monitoring works by scanning hidden sites and forums in real time to detect mentions of your data, credentials, or company information before cybercriminals can exploit them.
Q: Why use dark web monitoring?
A: Because it alerts you early when your data appears on the dark web, helping prevent breaches, fraud, and reputational damage before they escalate.
Q: Who needs dark web monitoring services?
A: MSSP and any organization that handles sensitive data, valuable assets, or customer information from small businesses to large enterprises benefits from dark web monitoring.
Q: What does it mean if your information is on the dark web?
A: It means your personal or company data has been exposed or stolen and could be used for fraud, identity theft, or unauthorized access immediate action is needed to protect yourself.
Q: What types of data breach information can dark web monitoring detect?
A: Dark web monitoring can detect data breach information such as leaked credentials, email addresses, passwords, database dumps, API keys, source code, financial data, and other sensitive information exposed on underground forums, marketplaces, and paste sites.


